May is Skin Cancer Awareness Month, and in most years, this is the time when people are starting to plan for summer vacations and spend more time outdoors. This means increased sun exposure, which is the leading cause of skin cancer. According to Dr. Sindy Pang at U.S. Dermatology Partners Bellaire, formerly Medical Center Dermatology, in Houston “Many states and local governments have mandated shelter in place orders during the month of May, so you may be thinking you don’t have to worry about sun exposure right now. Actually, more time at home doesn’t necessarily mean you’re decreasing your sun exposure or skin cancer risks. People should wear sunscreen every day, especially if they’re at high risk for skin cancers, even if they’re going to be indoors for the majority of the day.” In this blog, Dr. Pang discusses some of the reasons you should wear sunscreen every day and how to choose the best sunscreen for daily use.
The Link Between Sun Exposure & Skin Cancer
Skin cancer has been linked to a number of external factors, including repeated chemical exposure, genetics, and even friction. While skin cancer may be caused by one of these external factors, damage from the sun’s ultraviolet rays is by far the most common reason skin cancer develops. We’re all familiar with sun damage. Just about everyone has gotten a sunburn or suntan during their life. Whether you’re rubbing aloe on your sunburn or have bronzed skin after a tan, you’re seeing the results of UVA and UVB damage to your skin cells. In the short term, this may not seem harmful to your skin or your overall health. Unfortunately, temporary damage like sunburns is only one small part of more serious cellular damage that can occur due to sun exposure. Over time, cellular damage from UVA/B rays can lead to deep wrinkles, age spots, and even skin cancer. Sun exposure is almost exclusively the cause of the most dangerous form of skin cancer, melanoma, which makes it even more important to protect your skin from unnecessary UVA/B exposure.
Protect Against Indoor Sun Exposure
Many of us are spending a lot more time indoors these days, but that doesn’t mean you don’t get any sunlight. Most places of business have tinted windows that help protect people from unnecessary exposure, but your windows at home are not likely to be tinted, meaning unless you keep your curtains or blinds drawn the whole time you’re home, the UVA/B rays will get through. By applying sunscreen to your face, neck, hands, and other exposed areas, even when you stay indoors, you significantly minimize your risk. Additionally, many people are spending more time with their screens, and early research is indicating that the light from computers, smartphones, and TV screens may have an adverse impact on skin health. Fortunately, sunscreen can protect you from these potentially negative effects as well.
Combatting Cabin Fever with a Drive? Don’t Forget the Sunscreen!
When cabin fever starts to set in, many people are taking a drive to get out without risking their health or that of others. Driving in the car, you may not feel like you’re getting a lot of sun, but actually, the sunlight coming in through the windows can do some real damage. Make sure you’re applying sunscreen at least to your face, neck, arms, and hands. These areas are most likely to receive sun damage while you’re driving or riding in the car.
Take Safety Steps when Spending time in the Yard, Park, or on Walks
Another way many of us are getting out of the house is by working in the yard, practicing social distancing while visiting local parks, or going on walks in our neighborhoods. If you’re going to be outside, protect your skin by applying sunscreen to all exposed areas. Don’t forget to protect the top of your head. The scalp is also susceptible to sunburns. Wear a hat or apply a small amount of sunscreen to exposed areas of the scalp.
Prevent Small Problems that Could Develop into Serious Concerns
It may seem tedious to apply sunscreen every day, even if you’re not going outside, but this one, simple step can really help to keep your skin healthier. In addition to minimizing your risk for skin cancer, wearing sunscreen every day also helps prevent the development of age spots, fine lines, and wrinkles. Using the right kind of sunscreen can also keep your skin moisturized, which helps with chronic skin conditions like eczema.
Pick the Right Sun Protection Products
Developing any daily habit is hard, but if you’ve found yourself with a little more time on your hands without your daily commute, maybe now’s the perfect time to add sunscreen into your routine. Before you get started, make sure you’re choosing the right products to maximize the benefit.
Chemical VS Physical Sunblock
Chemical sunscreens, as the name implies, contain chemicals that absorb UVA/B rays and prevent them from reaching the skin. Physical sunblock contains ingredients like zinc oxide that create a physical barrier on the surface of the skin to deflect the sun’s rays. There has been a lot of debate about how safe different sunscreen options are and what kinds should be used for different skin types. Both chemical and physical sunscreens offer advantages and disadvantages that we’ll detail below.
Chemical Sunscreen Pros:
- Lightweight and easily absorbed for daily wear
- Pairs well with other daily skincare products
- Easy to wear under cosmetics
Chemical Sunscreen Cons:
- May irritate sensitive skin
- Can cause burning or itching in the eyes
- Need to wait at least 20 minutes before sun exposure to ensure efficacy
- Can increase redness for some rosacea sufferers
- Not all types are considered safe for every person – expectant mothers, infants, and toddlers should not use chemical sunscreens
Physical Sunblock Pros:
- Protects from both UVA and UVB rays
- Safe for use on any person (even infants, toddlers, and expectant mothers)
- Less irritating for sensitive skin and less likely to increase redness in rosacea sufferers
- Effective as soon as it’s applied, so there’s no need to wait before leaving home
Physical Sunblock Cons:
- Because it sits on the surface of the skin, it can rub or sweat off more easily, so you need to reapply more often
- Need to apply a thick coat to create an effective barrier, but that may mean your skin looks chalky
- The thickness of the application makes it difficult to wear under cosmetics without making skin appear flaky or creating lines or clumps
Sun Protection Factor
You should always choose a sunscreen that is broad-spectrum. That means it protects against both UVA and UVB rays. You should choose a sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher. Sunscreens with an SPF that’s less than 30 only moderately protect from sunburn and they do not protect against accelerated aging or skin cancer. SPF 30 sunscreens filter out 97% of UV rays. SPF 50 sunblock offers 98% protection, and SPF 100 sunscreens block 99% of UV rays. In short, no sunscreen will completely block out UV rays, but if you’re at greater risk or sunburn easily, higher SPF sunscreens are the way to go.
Reapply Regularly
Even sport or water-resistant sunscreens are not sweat or waterproof. They will stay on longer, but no matter what type of sunblock you use, you should be reapplying every two hours.
Check Your Skin Frequently for Areas of Concern
According to Dr. Pang, “If you are at high risk, have had skin cancer in the past, or you have numerous moles or freckles, you should check your skin for cancer at least once a month. If you’re at lower risk, every other month is okay, but everyone should be performing self-exams regularly. If something does change, you’ll know how quickly changes are occurring, which will help us determine your skin cancer risk.” You can find some basics about what to look for below, and you can use our “Mole Map” to keep track of any changes and areas of concern.
Warning Signs of the Most Common Types of Skin Cancer
There are many different types of skin cancer, and each has its own set of symptoms. The three most common are outlined below:
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) – Usually appears as a flesh-toned, round, bump or growth. In some cases, these may look like slightly raised patches of skin. BCC is typically found on the head, neck, and arms, but it may appear on any part of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) – May look like a red, firm bump, patch of scaly skin, or a sore that doesn’t heal completely. It most often develops on ears, face, neck, arms, chest, and back, but SCC can develop anywhere on the body.
- Melanoma – Often develops within an existing mole that will suddenly change in shape, color, or texture. It may also create a new dark spot or mole that seems to grow quickly. Melanoma may appear on any part of the body, including often overlooked areas like the nailbeds and bottoms of feet. This is the deadliest form of skin cancer, so catching and treating it early is essential.
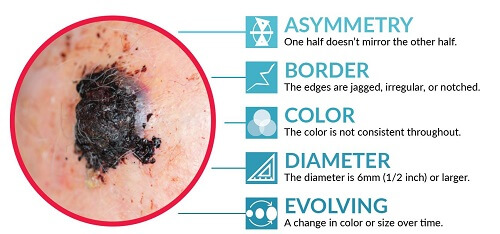
Know Your ABCDE’s
When it comes to spotting skin cancer, especially melanoma, you should start by learning the ABCDE’s:
A – Asymmetry – One part of a spot is not like the other in color, size, shape, or texture.
- B – Border – The spot’s border is irregular, jagged, or undefined.
- C – Color – The spot’s color is not like your other moles or dark spots or there are multiple colors in one mole.
- D – Diameter – The size of the spot is larger around than a pencil eraser.
- E – Evolving – The spot is changing in size, shape, color, or texture, especially if it’s changing quickly.
Visit Your Dermatologist for Checkups
Whether you’re looking for an annual skin examination, want tips on sun protection, or need help with potential skin cancer, the board-certified dermatologists at U.S. Dermatology Partners are here to help.
We make getting started easy. Simply fill out our online appointment request form to find a skilled dermatology team near you. Once we receive your request, we’ll be in touch to finalize the details of your appointment.
Find a location near me
or


 A – Asymmetry – One part of a spot is not like the other in color, size, shape, or texture.
A – Asymmetry – One part of a spot is not like the other in color, size, shape, or texture.