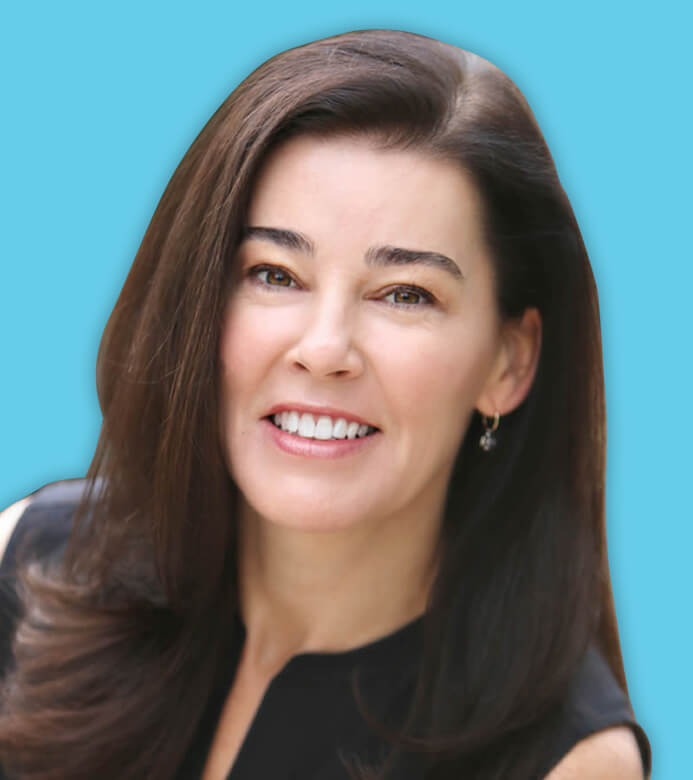
Dr. Amanda Rainwater joined Southwest Skin Specialists in 1998. After attaining her undergraduate degree from the University of Virginia in 1989, Dr. Amanda Rainwater earned her medical degree from George Washington University in 1994. Her postgraduate training included an internal medicine internship at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, and a residency in dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Dr. Amanda Rainwater practices general medical dermatology at Southwest Skin Specialists and she is also an associate professor with Creighton University School of Medicine. She treats skin conditions such as acne, skin cancer, and hair loss.
Dr. Amanda Rainwater provides dermatology care to patients in Scottsdale and Phoenix, Arizona at Southwest Skin Specialists, now a part of U.S. Dermatology Partners.
Specialties and Affiliations
- Fellow, American Academy of Dermatology
- Member, Scottsdale Women Physicians Group
- Member, Phoenix Dermatologic Society
Badges and Awards
- PHOENIX Magazine’s Top Doctors Honors