Sun Damage Treatments from U.S. Dermatology Partners
What Is Sun Damage?
The sun can age and burn your skin, and it can also cause damage on the cellular level, leading to skin cancer. The good news is, the U.S. Dermatology Partners team can help you formulate a plan to prevent sun damage and repair the effects of the sun’s UV rays so that you can go out and enjoy a sunny day. Learn more on this page or contact U.S. Dermatology Partners to schedule an appointment with us.
Find This Service Near You
What Is Sun Damage?
Sun damage occurs when the skin is exposed to the ultraviolet (UV) rays of sunlight. Over time, repeated or extended exposure to the sun creates cumulative damage to the skin, so it’s important for everyone to take steps to protect their skin from the sun’s damaging rays at all ages.
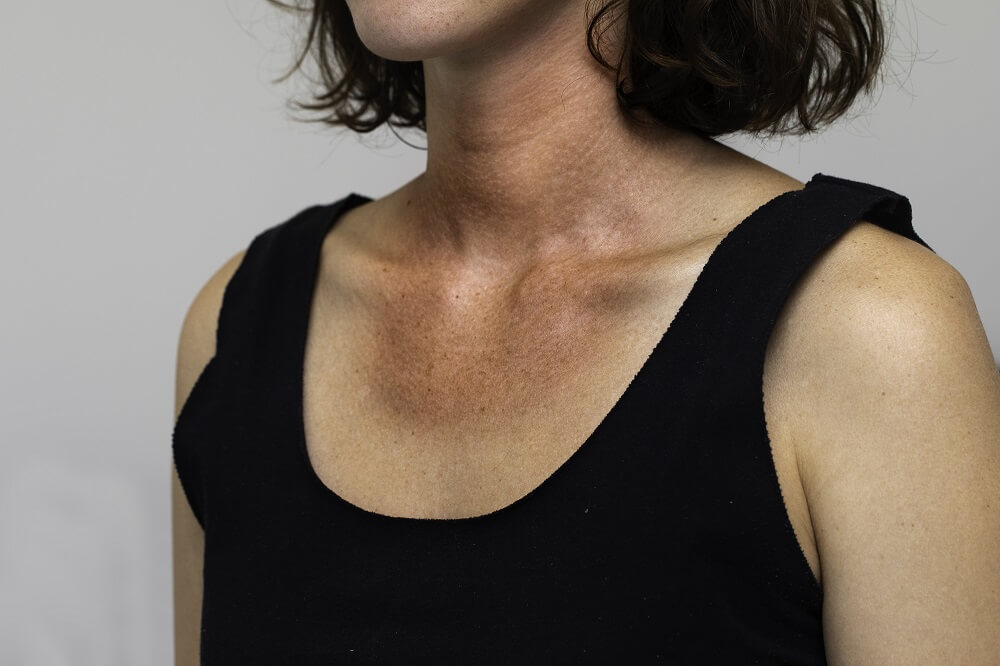
- Sunburns – The most immediate form of sun damage, sunburns can be extremely painful, and without proper treatment, these burns can lead to scarring or infection. Additionally, frequent sunburns increase the risk of developing the other two most common forms of sun damage – accelerated aging and skin cancer.
- Accelerated aging – The sun’s ultraviolet light breaks down and damages the collagen and elastin in our skin. When this happens, the skin begins to lose its ability to go back into place after stretching or moving, causing it to sag and wrinkle.
- Skin cancer – When the DNA in skin cells are damaged, the body may begin to reproduce these damaged cells in irregular ways. While healthy cells reproduce in predictable ways, damaged cells can produce in unexpected and potentially harmful ways. These damaged cells are considered cancerous, and in some cases, they can damage the surrounding skin cells and tissues as well as metastasizing to impact unconnected tissues.
Who Is at Risk for Sun Damage?
Anyone can be affected by sun damage, but certain factors may dramatically increase your risk for sun damage, including:
Light skin tones – Those with lighter skin tones produce less melanin, which reflects the UV rays. Without the protective melanin, skin cells are much more susceptible to damage from UVA/B rays.
- Those with moles and freckles – Because melanoma, the most serious form of skin cancer, often develops within moles, those who already have moles and freckles may be at higher risk to develop this type of skin cancer after sun exposure.
- Cumulative sun exposure – Repeated, long term sun exposure has a cumulative impact on skin health. Repeatedly experiencing sunburns, working outdoors, tanning, living in a tropical climate, and other situations that expose the skin to excessive sunlight all increase the risk for sun damage.
- Altitude – Living or spending time in high altitude areas exposes you to the sun’s UVA/B rays at an increased intensity, which is a risk factor for skin cancer.
- Genetics – A personal or family history of struggles with sun damage usually means individuals are at greater risk for these concerns.
- Autoimmune disease – Lupus, HIV, and other conditions that weaken the immune system put you at greater risk for sun damage and can make it more difficult for your skin to heal after the damage occurs.
- Medications – Certain medications make your skin more sensitive to the sun’s rays and increase your risk for sun damage.
Sun Damage Symptoms
Symptoms of sun damage can occur at various stages and at different levels of severity for each individual.
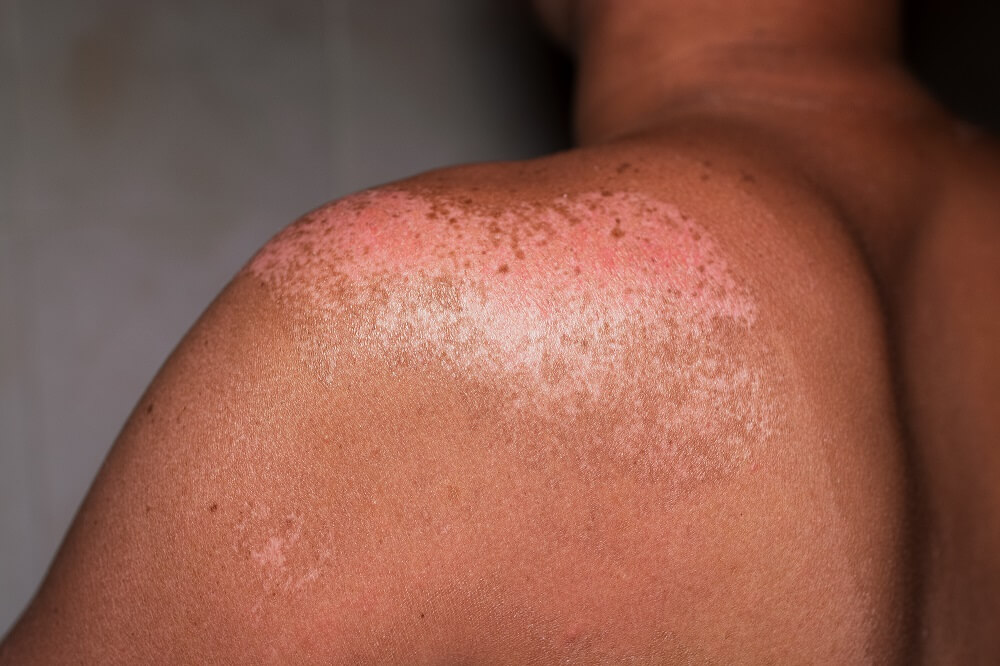
- Dry skin
- Sunburn
- Long-term changes in the skin like deep wrinkles and thickening of the skin’s texture
- Easy bruising on the back of the hands and forearms
- Actinic keratosis, a small bump that feels like sandpaper or a persistent patch of scaly (peeling) skin with a jagged surface
The long term effects of sun damage include premature aging of the skin, such as the formation of fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots. Additionally, you may notice evolving spots or moles on the skin and other signs of skin cancer caused by sun damage.
Sun Damage Treatments
If your skin has been damaged by the sun, the physicians at U.S. Dermatology Partners can evaluate which treatments will best help your skin’s recovery. The type of treatment for sun damage will depend upon the form of sun damage.
Specifically, we may recommend the following treatments for specific types of sun damage:
- Sunburn – Use a moisturizer and also avoid hot baths and showers. Apply cool compresses and a light topical treatment of aloe vera gel.
- Accelerated aging – Long-term sun damage that causes collagen changes cannot be reversed, but your dermatologist can provide you with options to improve the appearance of your skin. These may include daily products such as antioxidants and retinoids, or treatments such as chemical peels, cryosurgery, laser resurfacing, or dermabrasion.
- Skin cancer – Most forms of skin cancer are responsive to treatment. In many cases, we can remove the damaged tissues using minimally invasive techniques like Mohs micrographic surgery.
Sun Damage Prevention
Preventing sun damage isn’t always possible, but there are certain steps you can take to limit UVA/B exposure and reduce your risk for skin cancer and other serious long term effects, including:
Sunscreen – Everyone needs to be applying sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher each day. Many daily-use body lotions and facial moisturizers have built-in sunscreens, which can help you streamline your daily routine while ensuring your skin is protected. If you’re outside for extended periods, make sure you’re reapplying sunscreen at least every two hours.
- Avoid sun exposure during peak hours – Between 10 am and 4 pm, the sun’s rays are more direct and can have the most damaging effects, so limit your time outdoors during these hours.
- Protective gear – Don’t forget to wear sunglasses, gloves, hats, and other items that will protect those parts of the body that are most likely to receive sun exposure. You may also want to wear long sleeves and pants, even when it’s warm outside, to avoid unnecessary sun damage.
- Take breaks – Go inside, sit under an umbrella, or otherwise seek shade periodically when you’re spending extended time outdoors.
Limiting the Impact of Sun Damage with Self-Exams & Annual Professional Exams
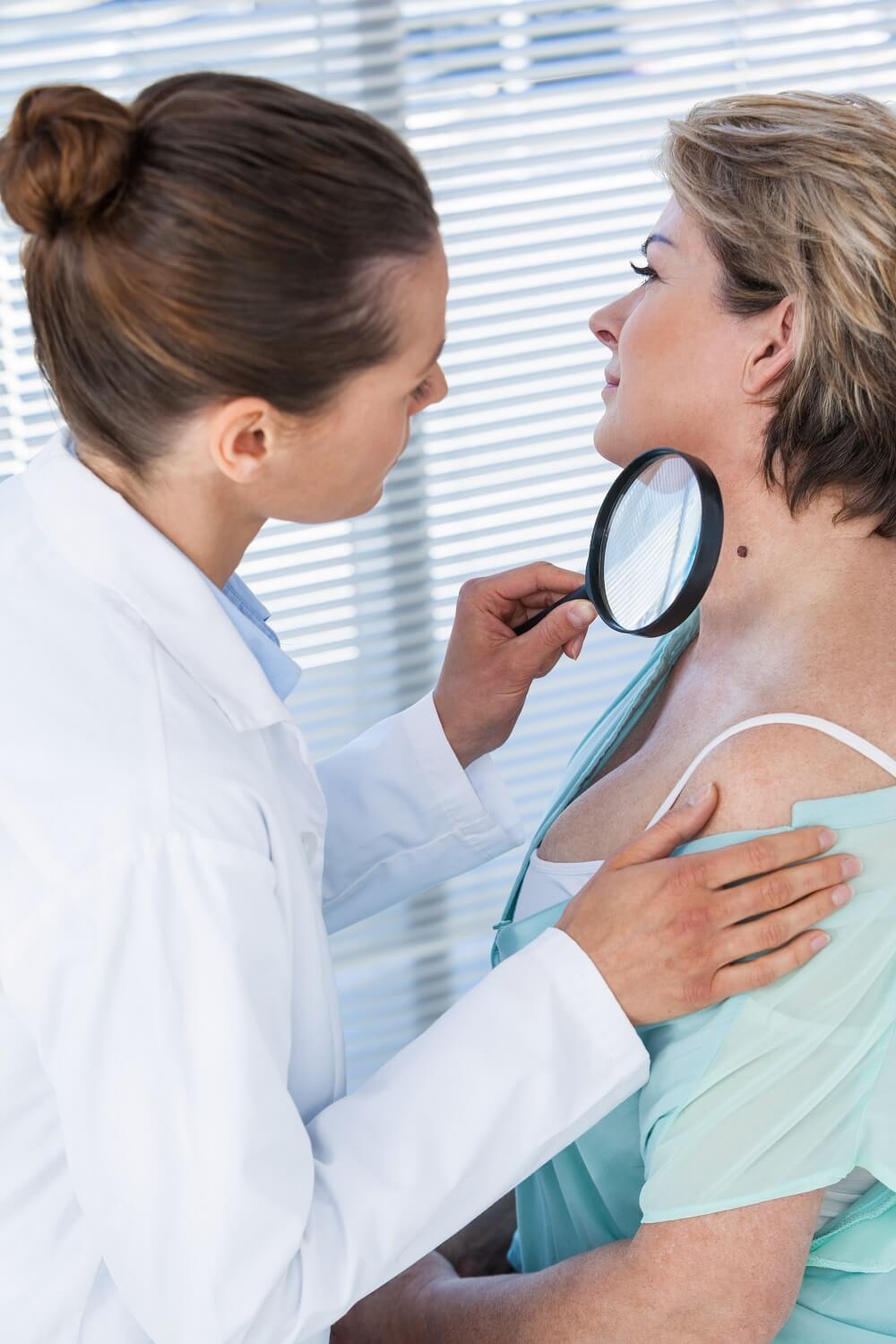
Additionally, we provide a skin cancer self-assessment chart from the American Academy of Dermatology that allows people to track any new or changing spots or irregularities on their skin.
Some tips to keep in mind during your skin health self-assessment include:
- Use good lighting so that you can see your skin clearly.
- Use a full-length mirror to help you see any irregularities on the front of the body.
- Use a hand mirror to see the back of the body and any other difficult to view areas.
- Start from the top and work your way down your body – front, back, and sides.
- Don’t forget to check your scalp, around your fingernails and toenails, and on the palms of hands and soles of feet.
- Flex at any joints (wrists, ankles, knees, and elbows) and look for any pulling or pitting that may indicate an area of concern.
*Results may vary by individual
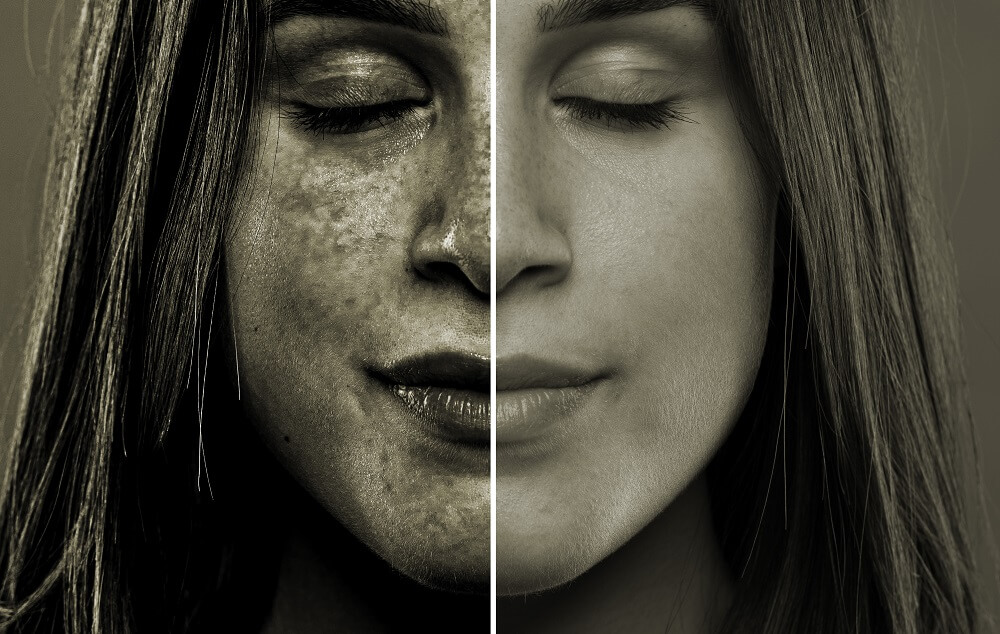


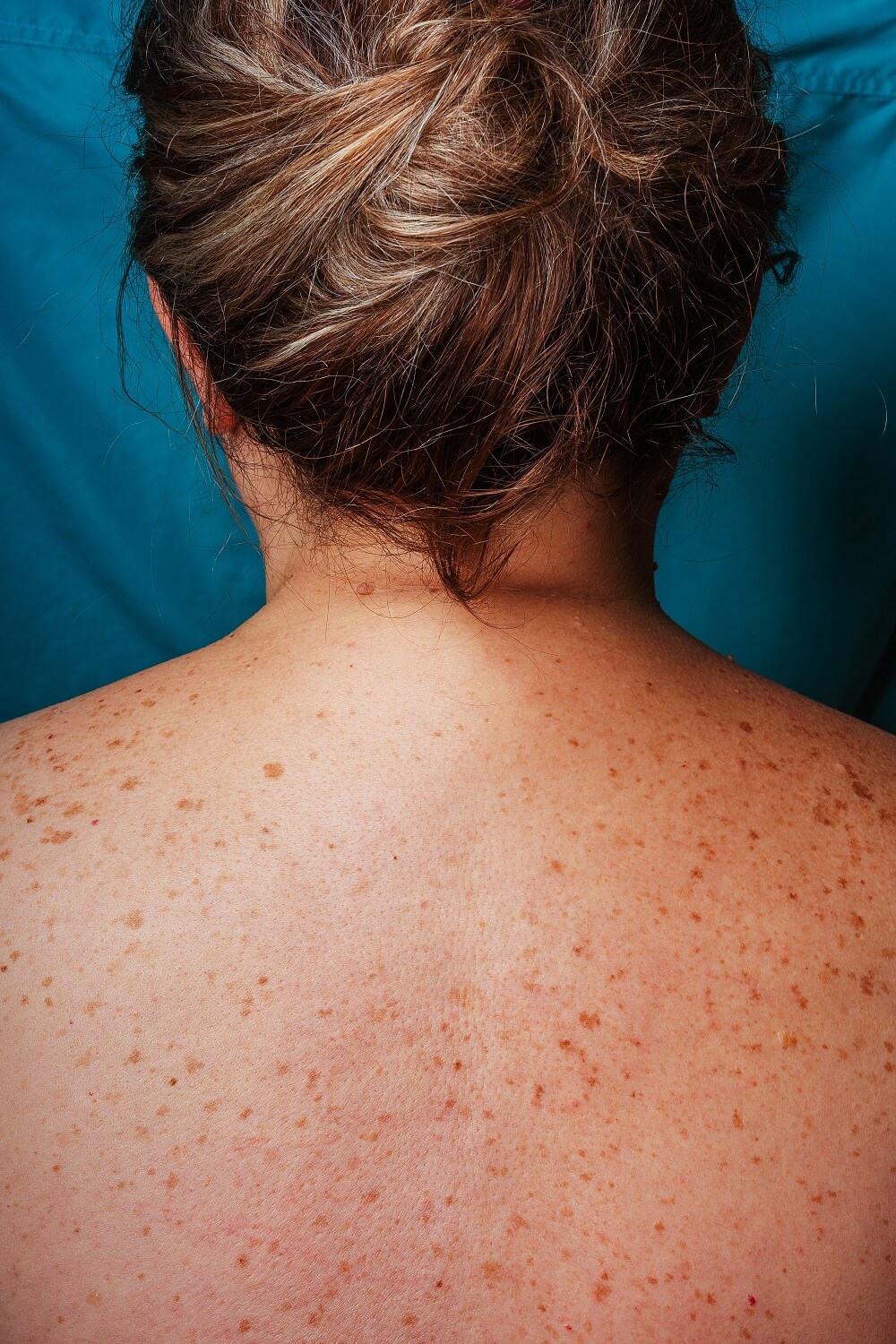 Light skin tones – Those with lighter skin tones produce less melanin, which reflects the UV rays. Without the protective melanin, skin cells are much more susceptible to damage from UVA/B rays.
Light skin tones – Those with lighter skin tones produce less melanin, which reflects the UV rays. Without the protective melanin, skin cells are much more susceptible to damage from UVA/B rays.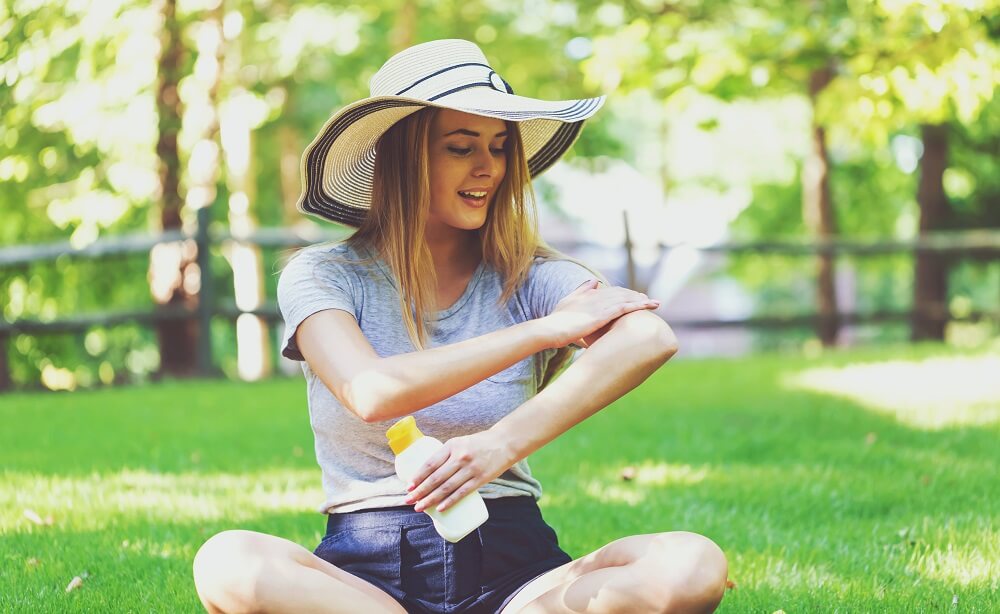 Sunscreen – Everyone needs to be applying sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher each day. Many daily-use body lotions and facial moisturizers have built-in sunscreens, which can help you streamline your daily routine while ensuring your skin is protected. If you’re outside for extended periods, make sure you’re reapplying sunscreen at least every two hours.
Sunscreen – Everyone needs to be applying sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher each day. Many daily-use body lotions and facial moisturizers have built-in sunscreens, which can help you streamline your daily routine while ensuring your skin is protected. If you’re outside for extended periods, make sure you’re reapplying sunscreen at least every two hours.