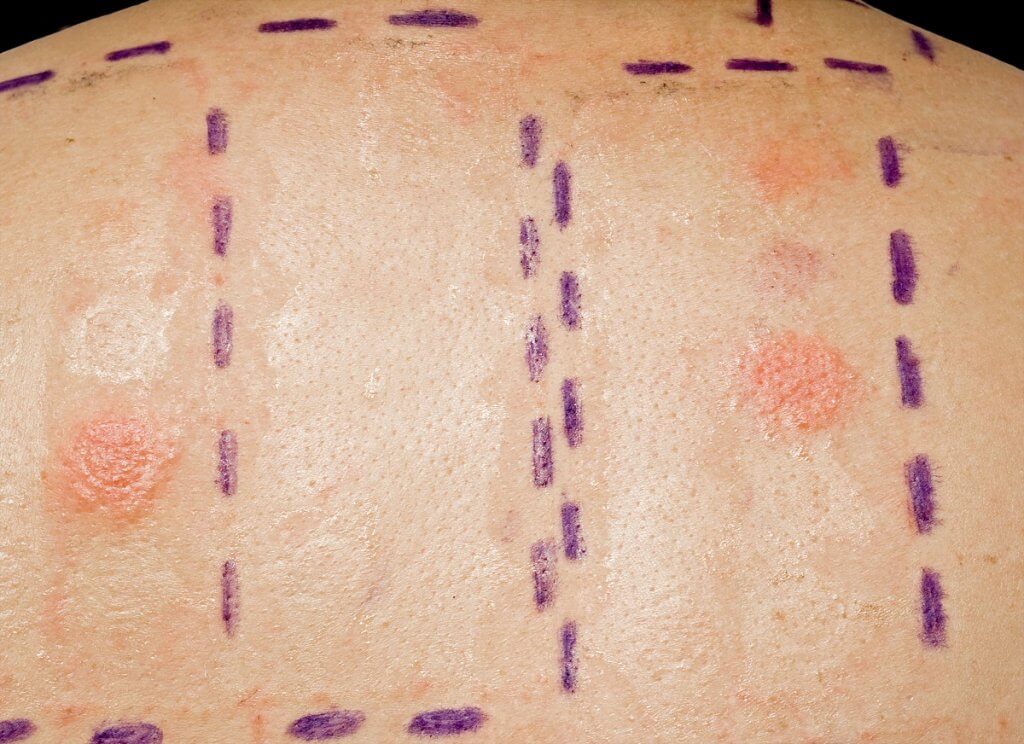
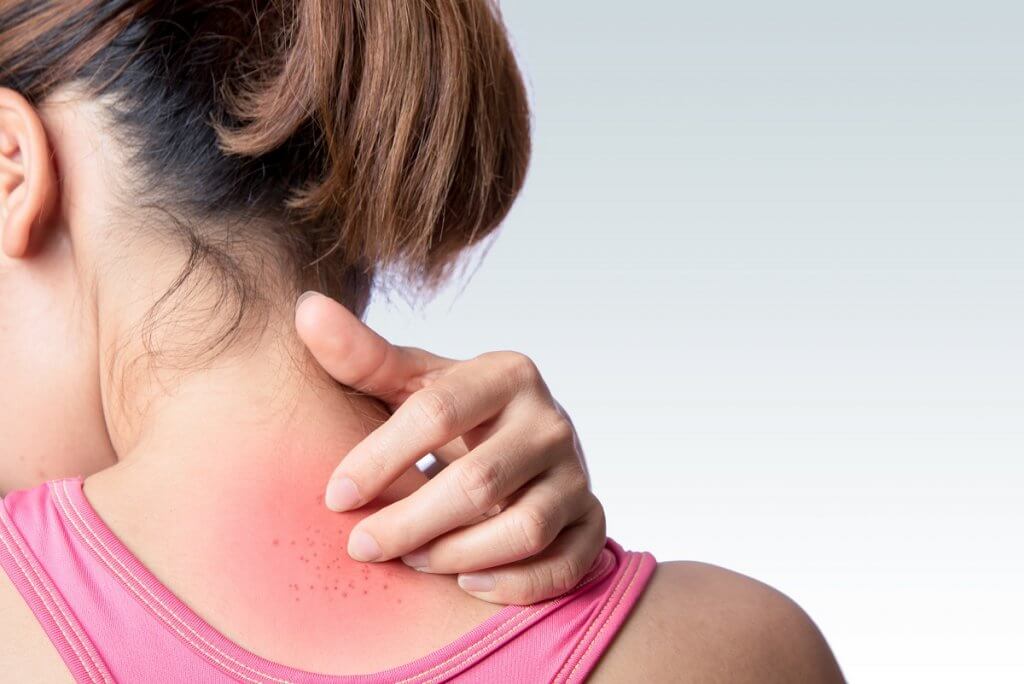
Allergy Patch Testing at U.S. Dermatology Partners
Discover the Sources of Your Allergies
A dermatologist may recommend allergy patch testing to pinpoint the sources of allergic skin response. These tests can help you to avoid allergens and improve your skin and overall health. You can learn more about allergy patch testing at U.S. Dermatology Partners on this page or by contacting the location nearest you to schedule a consultation with one of our knowledgeable dermatologists.
Find This Service Near You
What is Allergy Patch Testing?
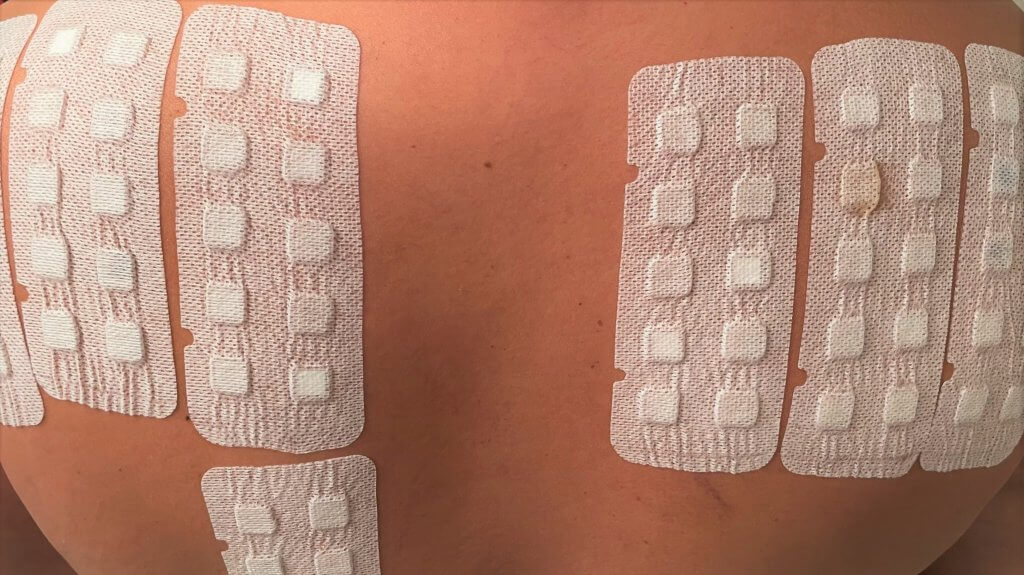
Allergens that will impact individuals when inhaled, eaten, or taken as a medication are determined through skin prick tests and skin injection tests. Skin prick tests check for a range of different allergens by placing a small dose of the potential allergen just below the skin. Skin injection tests are specifically used for insect venom and penicillin, and they involve injecting a controlled dose of the substance a little deeper into the skin. You will know the results of these types of allergy tests within an hour, and you should be able to create a treatment plan right away.
Allergy patch testing works a little differently. The potential skin allergens are applied to the skin’s surface using adhesive patches. These patches are worn for 24 to 48 hours before you return to the office to allow the dermatologist to check for signs of an allergic response. You will then return 48 hours later for a second exam of the patch test area. Allergy patch tests will also help patients understand the severity of their allergy to determine an appropriate treatment plan. Some mild allergies may require the individuals to avoid their allergen or take over-the-counter allergy medication. More severe allergic responses might necessitate prescription medications, allergy shots, or require the allergic person to carry an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) with them.
Who is a Good Candidate for Allergy Patch Testing?
Allergy patch testing is a procedure that is safe for adults and children. Even infants can safely receive allergy patch testing. In some rare cases, patients may not be a good candidate for allergy patch testing, including:
- Those who have had a severe allergic response in the past as this increases the risk for an extreme response to even the small amounts of allergens used in patch testing
- Individuals who are taking medications that could interfere with results, including allergy medications, antihistamines, steroids, some antidepressants, and heartburn treatments
- Patients who do not have a large enough area of healthy skin on which to apply the patch
Allergy patch tests may be recommended to diagnose allergic skin responses to a wide range of substances, including:
- Latex
- Fragrances and perfumes
- Dyes
- Medications
- Metals
- Preservatives
- Plants
How Does Allergy Patch Testing Work?
Before you receive an allergy patch test, your dermatologist will want to complete a thorough review of your medical history, including medications (both prescription and over-the-counter), allergy symptoms or reactions that prompted your visit, and methods you’ve used to address allergies in the past. This consultation process helps the dermatologist to understand your situation and plan for the safest and most effective allergy testing plan.
If you have a current allergy flareup, the dermatologist may also examine you to see the severity of your response. To achieve clear results from allergy patch testing, your dermatologist will likely ask you to stop taking certain medications that can interfere with the results. For this reason, it’s very important to tell your dermatologist about all medications you take, even over-the-counter medicines. The effects of medications are processed out of the body at different rates, so your dermatologist may ask you to abstain from taking them at different times. You may need to forego certain medications for as long as two weeks.
When it’s time for the procedure itself, your allergy patch test appointment is usually relatively short. The allergy patch test is centered upon determining the source of skin inflammation and irritation (an allergic skin response called allergic contact dermatitis) based on controlled contact with an allergen. The allergy patch test is used to detect delayed allergic response, so you will not have the results before you leave. Unlike the other types of allergen testing that use needles to administer the allergen beneath the skin, patch testing applies common allergens to the skin using adhesive patches. Using the patches, a dermatologist administers small doses of numerous potential allergens to determine the likely cause of any allergic skin reactions. You’ll need to keep the patches on your skin for about 48 hours, which means changing your activities to avoid getting the patches wet.
Are There Side Effects to Allergy Patch Testing?
The side effects of allergy patch testing depend on the individual. If you aren’t allergic to any of the substances you’re exposed to, you may have some redness or inflammation at the testing site, but you shouldn’t have any other issues.
If you are allergic to one or more of the substances being tested, you’ll experience some of the common symptoms of allergic response, including:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Itching
- Bumps (hives)
These common symptoms may take a few hours or days to develop, and the response can last anywhere from several days to a week. While it’s very rare, an allergy patch test can lead to a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). This almost always occurs soon after the patch test is administered while you’re still under the care of your dermatologist who will take immediate action to get the proper treatment. If you notice signs of a severe allergic response after you leave the dermatologist’s office, including spreading or worsening rash or difficulty swallowing or breathing, you should seek emergency medical care right away.
Will I Ever Need to be Retested?
If your allergy patch test is inconclusive in some way, the dermatologist may want to retest to confirm an unclear diagnosis. Additionally, allergies can develop and change throughout your lifetime. If you suspect you’ve developed a new allergy or that you may have stopped reacting to an allergen, your dermatologist may recommend retesting.
*Results may vary by individual