Melanoma Treatments from U.S. Dermatology Partners
What Is Melanoma?
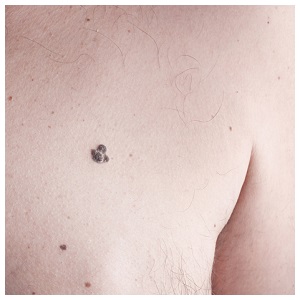
Melanoma, the deadliest of skin cancers, only accounts for about 4 percent of all skin cancer cases, but causes about 79 percent of skin cancer deaths.
Melanoma is a cancer of the skin that begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that produce the pigment melanin. It is the leading cause of cancer death in women 25 to 30 years old and the second leading cause of cancer death in women 30 to 35 years old.
In some cases, melanoma occurs in melanocytes throughout the body, even if those parts have never been exposed to the sun.
Find This Service Near You
Who Is at Risk for Melanoma?
Since 90% of melanoma cases can be linked to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from natural or artificial sources such as sunlight and indoor tanning beds, people who have extended or frequent exposure to these rays are at greater risk.
The World Health Organization has declared indoor tanning devices to be cancer-causing agents in the same category as tobacco. Studies have found a 59% increase in the risk of melanoma in those who have been exposed to UV radiation from indoor tanning.
Family history, genetics and environmental factors are also considered strong risk factors for melanoma. People with light eyes, hair, and/or skin, sun sensitivity, a high number of moles, a history of sunburns, a previous melanoma diagnosis or those who have a weakened immune system are also at greater risk.
If you have an increased risk of developing melanoma, you must be particularly vigilant and become aware of all of the moles on your body to minimize the risk of melanoma progressing to life-threatening stages.
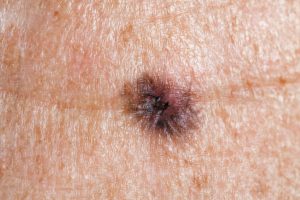
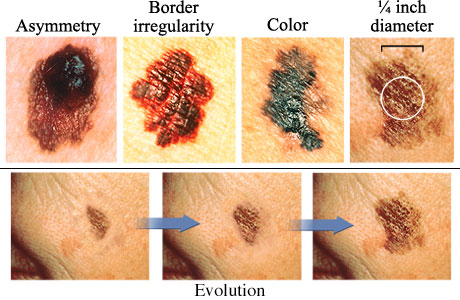
Melanoma Symptoms

- A sore that doesn’t heal.
- Pigment that spreads from the border of a spot into surrounding skin.
- Redness or swelling beyond the border of the mole.
- Itchiness, tenderness or pain.
- A change in the mole’s surface, such as scaliness, oozing, bleeding or the appearance of a lump or bump.
Melanoma Treatments
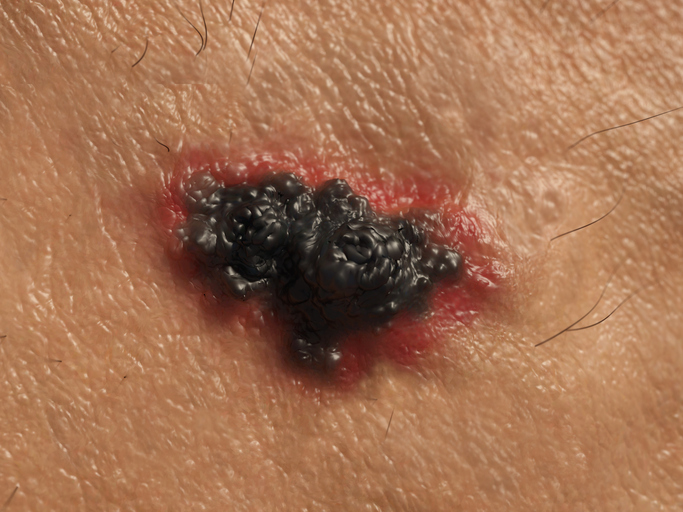
Melanoma skin cancer has a bulbous, black appearance.
Treatment for melanoma depends primarily on what stage it is when discovered. Early stage cancer is the easiest to treat, and will often be treated by surgery alone. However, if the cancer is more advanced, your doctor may also recommend immunotherapy, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, which uses high-energy beams such as X-rays to kill cancer cells.
Melanoma Prevention

Wearing long sleeves in sunlight can help prevent exposure to harmful UV rays. Also avoid being outdoors during peak times of sun.
Since most melanoma and non-melanoma cases are directly related to sun exposure, the best way to prevent skin cancer is to protect your skin from sunlight. Make smart sun habits a part of your daily healthcare regimen.
- Limit the amount of time spent outdoors during peak sun hours (10:00 AM to 4:00 PM).
- Avoid tanning booths and sunburn.
- Wear a broad spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with an SPF of 15+ every day.
- For extended outdoor activity, use a water-resistant, broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30+.
- When outside, cover-up with long pants, a long-sleeved shirt, a broad-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Check your skin head-to-toe every month.
- See your dermatologist every year for an annual skin examination.
*Results may vary by individual